TL;DR: A generic unified anomaly detection framework designed for diverse domains and settings,
with key elements of effective feature selection and contrastive learning-guided anomaly discrimination.
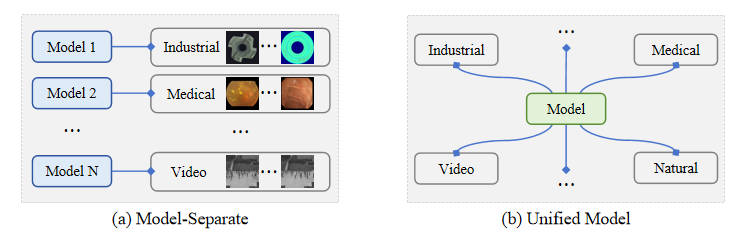
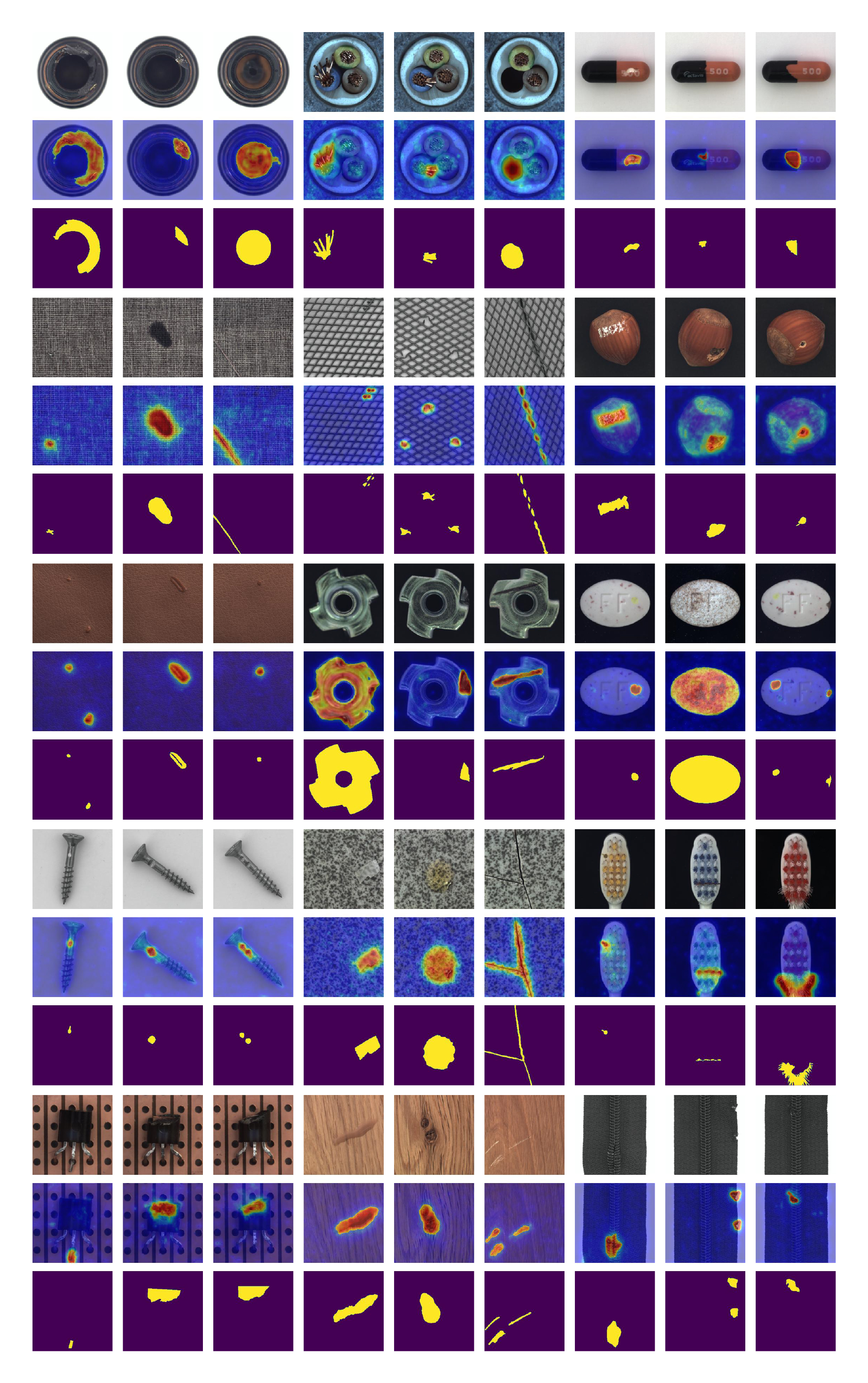
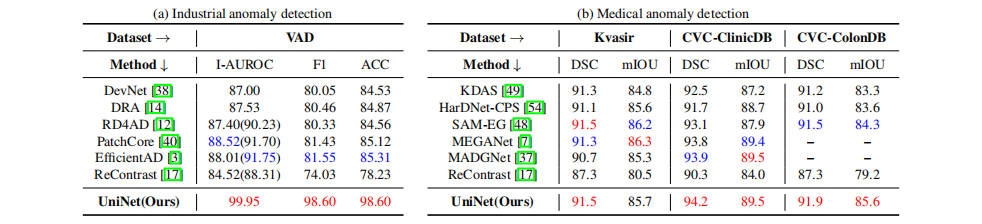
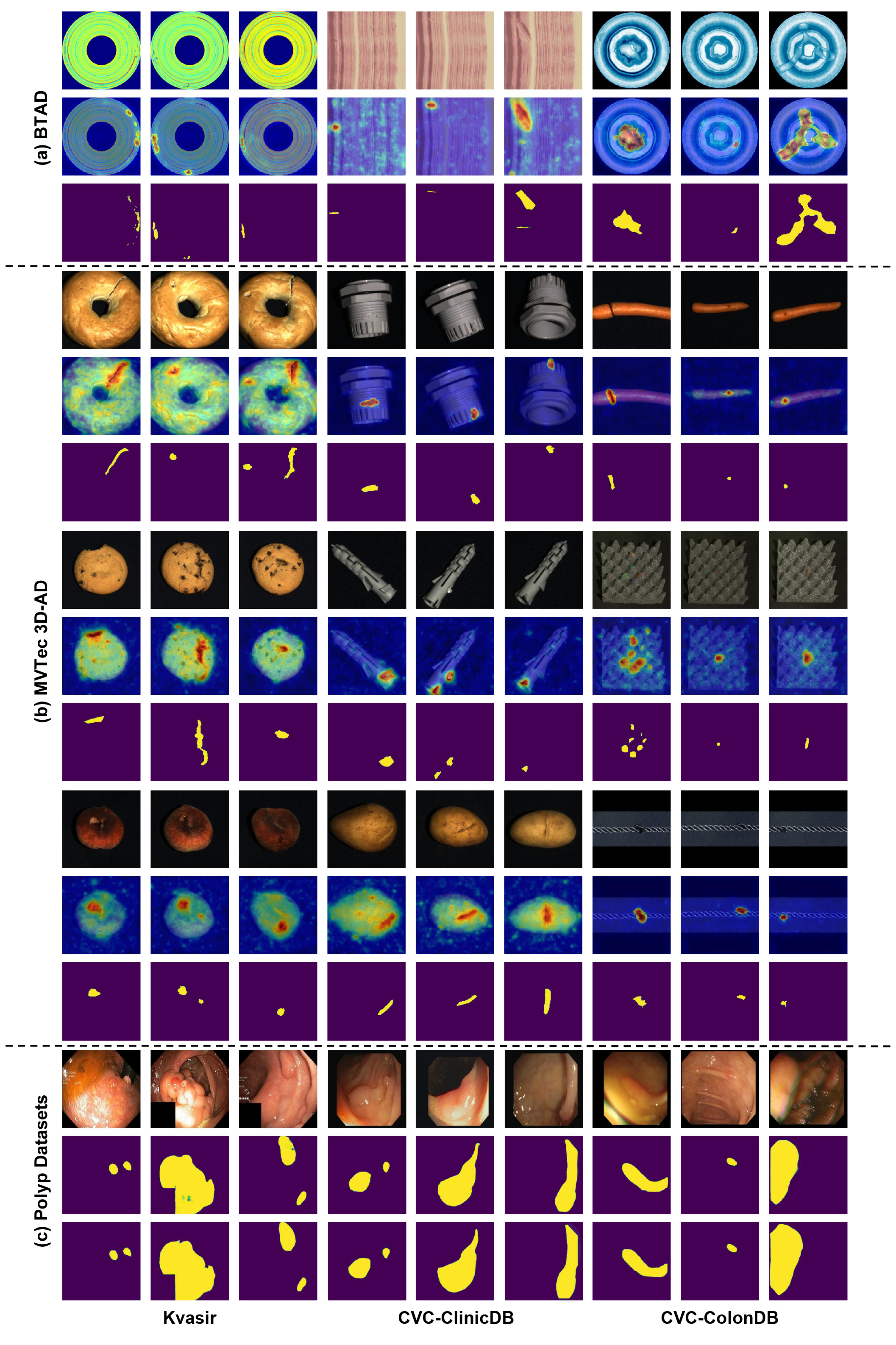
Anomaly detection (AD) is a crucial visual task aimed at recognizing abnormal pattern within samples. However, most existing AD methods suffer from limited generalizability, as they are primarily designed for domain-specific applications, such as industrial scenarios, and often perform poorly when applied to other domains. This challenge largely stems from the inherent discrepancies in features across domains. To bridge this domain gap, we introduce UniNet, a generic unified framework that incorporates effective feature selection and contrastive learning-guided anomaly discrimination. UniNet comprises student-teacher models and a bottleneck, featuring several vital innovations: First, we propose domain-related feature selection, where the student is guided to select and focus on representative features from the teacher with domain-relevant priors, while restoring them effectively. Second, a similarity contrastive loss function is developed to strengthen the correlations among homogeneous features. Meanwhile, a margin loss function is proposed to enforce the separation between the similarities of abnormality and normality, effectively improving the model's ability to discriminate anomalies. Third, we propose a weighted decision mechanism for dynamically evaluating the anomaly score to achieve robust AD. Large-scale experiments on 12 datasets from various domains show that UniNet surpasses state-of-the-art methods.
Overview framework of the proposed UniNet. It consists of a pair of teachers models, a bottleneck, and a student model, with several key components: Multi-scale Embedding Module (MEM), Domain-related Feature Selection (DFS), Similarity-Contrastive loss \( \mathcal{L}_\mathit{SC} \), and Margin loss \( \mathcal{L}_\mathit{M} \).
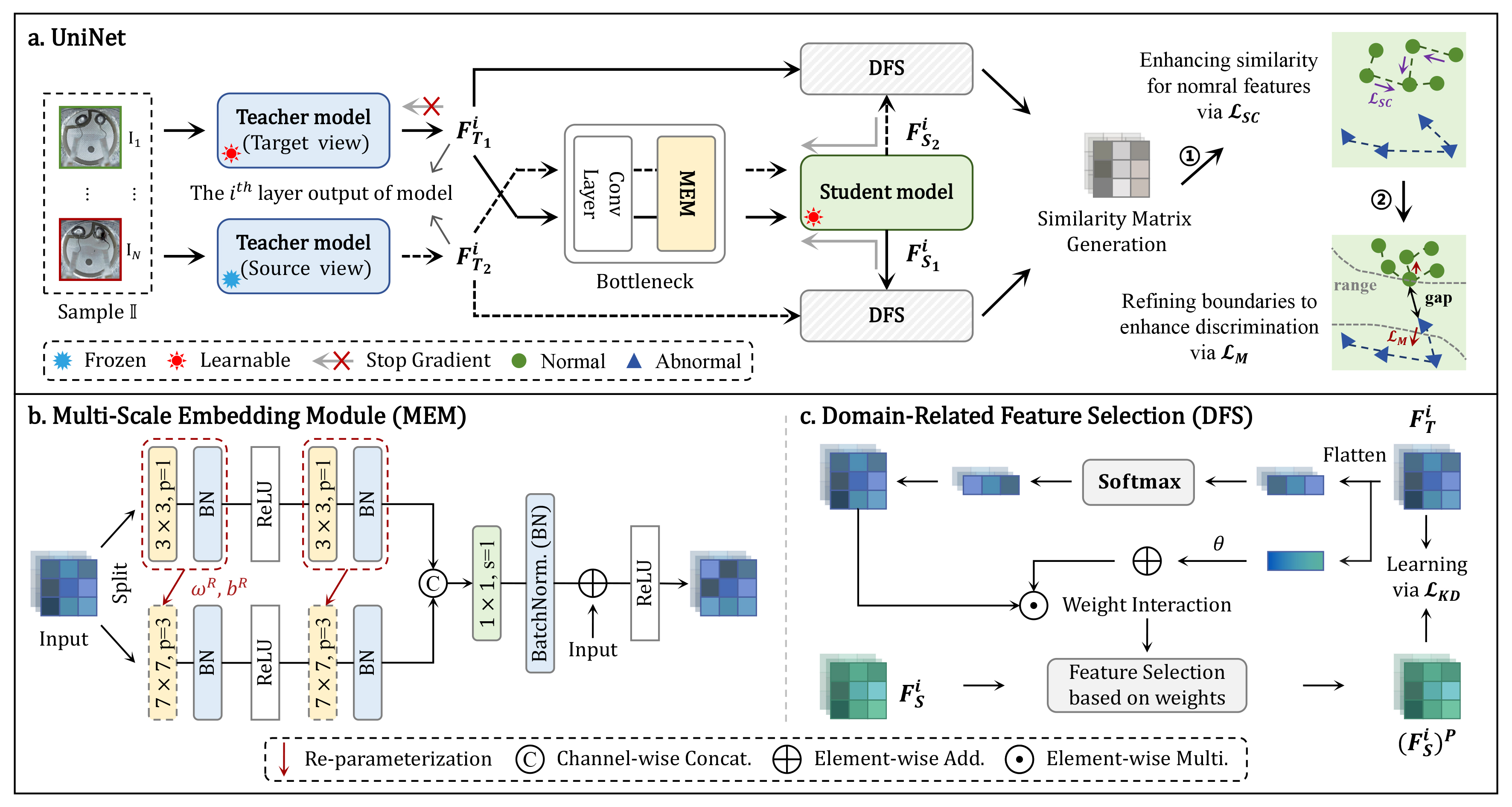
We design a multi-scale embedding module to effectivel capture the contextual relationship among features provided to the student.
To mitigate the computational overhead introduced by large kernels, we reparameterize them through small kernels and batch normalization (BN) layers.
We propose domain-related feature selection to encourage the student to selectively concentrate on target-oriented features from the teacher and well restore them, where the weight is used to control how much representative information should be selected from the teacher with prior knowledge.
We introduce two loss functions to first maximize the similarity for normal features (\( \mathcal{L}_\mathit{SC} \)),
and then enhance separation effect by maintaining the similarity for normal features above a range while
decreasing it for abnormal ones (\( \mathcal{L}_\mathit{M} \)).
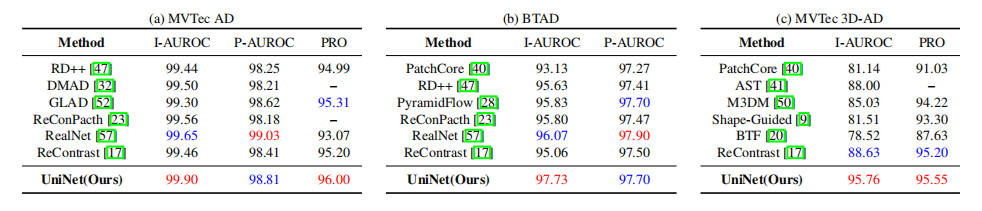
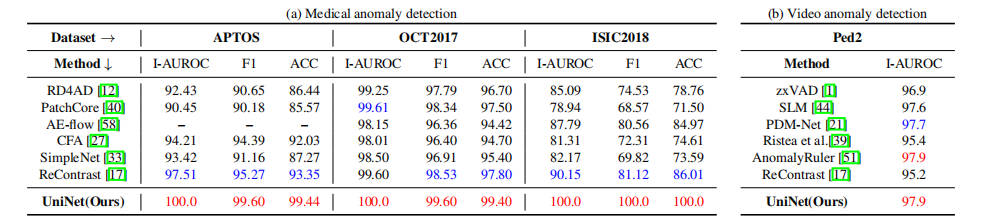

@article{wei2025uninet,
title={UniNet: A Contrastive Learning-guided Unified Framework with Feature Selection for Anomaly Detection},
author={Wei, Shun and Jiang, Jielin and Xu, Xiaolong},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition},
year={2025}
}